Description
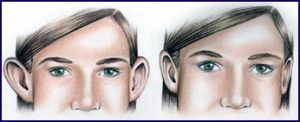
Reduces the size of large ears or sets prominent ears back closer to the head. Ear surgery is commonly done on children between ages 4 and 14 years old.
Length
2 to 3 hours.
Side Effects
Temporary throbbing, aching, swelling, redness and numbness (patients are advised not to sleep on their sides in order to reduce ear pressure.)
Recovery
Back to work or school: 5 to 7days. Strenuous activity and contact sports: 1 to 2 months.
Risks
Infection of cartilage, excess scarring, blood clots. Mismatched or artificial-looking ears. Repeat surgery to correct recurrence of protrusion.
Results
Usually permanent.
Technology
The type of incisions used for ear surgery will depend on the problem, and even when only one ear appears to protrude, surgery is usually performed on both ears for a better balance. For one of the common techniques, a surgeon makes a small incision in the back of the ear to expose cartilage, then sculpts the cartilage, bending it back toward the head; occasionally removing a larger piece of cartilage to provide a more natural-looking fold. Another technique involves a similar incision in the back of the ear, skin removal, and stitches used to fold the cartilage back on itself to reshape the ear without removing cartilage.
Patient Status
Outpatient
Anesthesia
General

 فارسی
فارسی

بدون دیدگاه